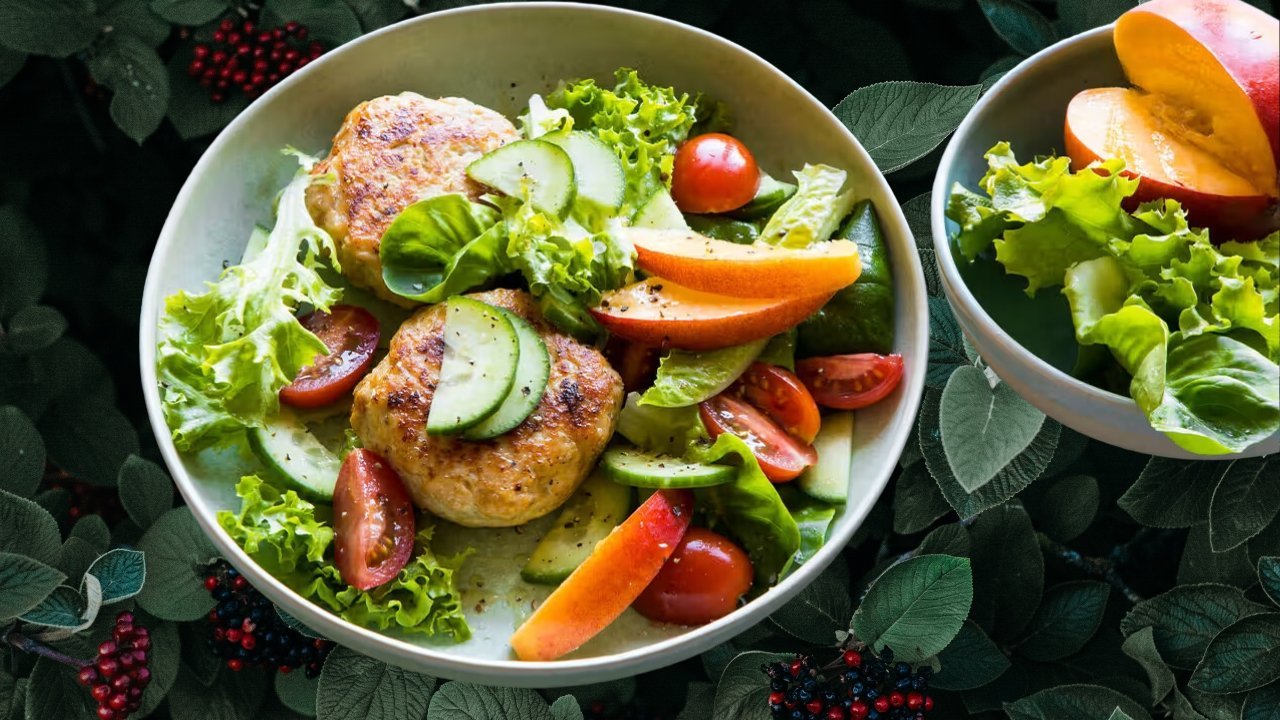Gastrointestinal Soft Diet Food List: Heal Fast Now!

When digestive problems arise, what you consume can considerably impact your comfort and recovery. The gastrointestinal soft diet food list is a crucial manual for everyone recovering from digestive surgery, coping with chronic gastrointestinal conditions, or simply looking to soothe an irritated digestive tract. This diet emphasizes easy-to-digest foods that minimize irritation and promote healing, making it a cornerstone in many American families managing digestive health challenges. Understanding what foods to include and why they matter can empower you to make better dietary choices during these sensitive times.
Understanding the Gastrointestinal Soft Diet Food List
The gastrointestinal soft diet is designed to reduce strain on the digestive system by focusing on foods which are low in fiber, bland, and easy to chew and swallow. Typically prescribed after gastrointestinal surgery or during flare-ups of conditions like gastritis, ulcers, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), this diet helps to avoid stressing the gut lining while still providing essential nutrients.
Unlike everyday diets, the soft diet excludes foods that are difficult to digest including tough meats, raw vegetables, and spicy foods. Instead, it prioritizes cooked vegetables, tender proteins, and refined grains. The goal is to provide nourishment while minimizing symptoms like bloating, cramping, and diarrhea.
“A carefully planned soft diet can significantly reduce gastrointestinal symptoms and assist healing, but it must be balanced to avoid nutritional deficiencies.”
— Dr. Emily Watson, Gastroenterologist at the Mayo Clinic
The Core Components of a Soft Diet for Gastrointestinal Health
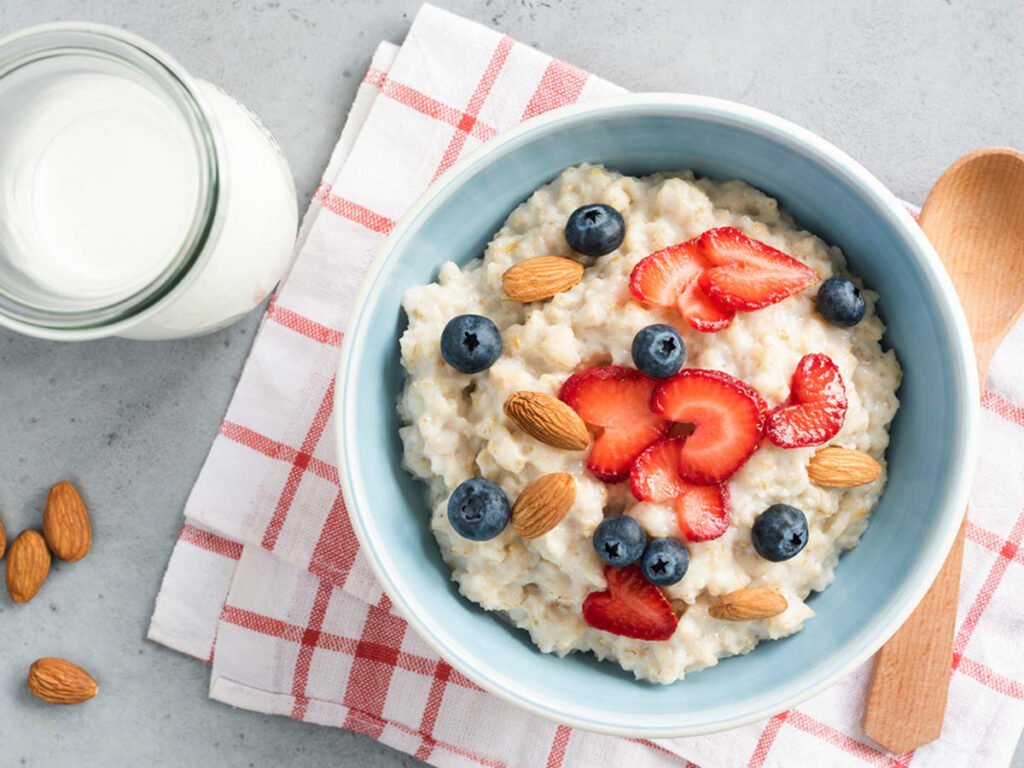
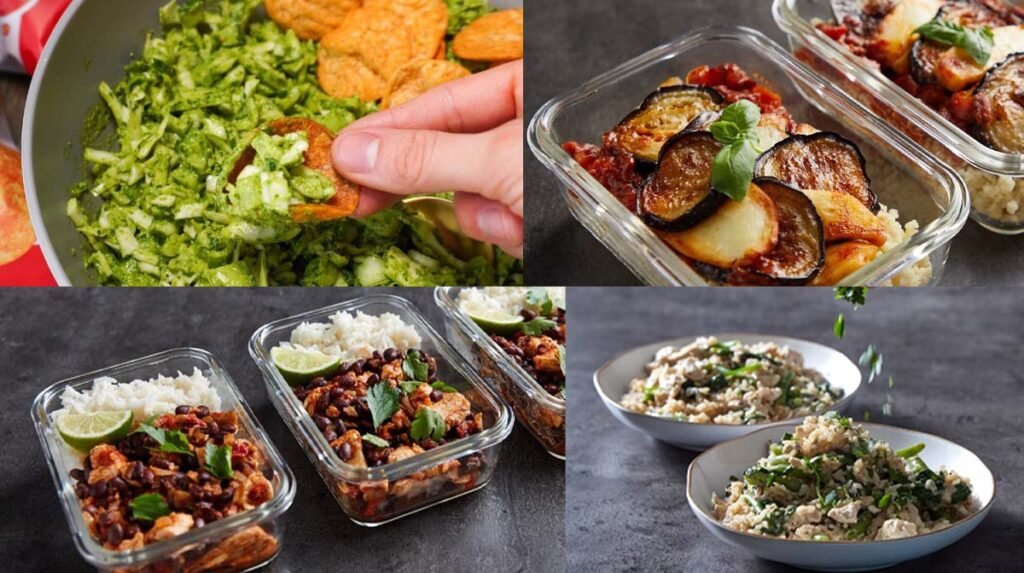
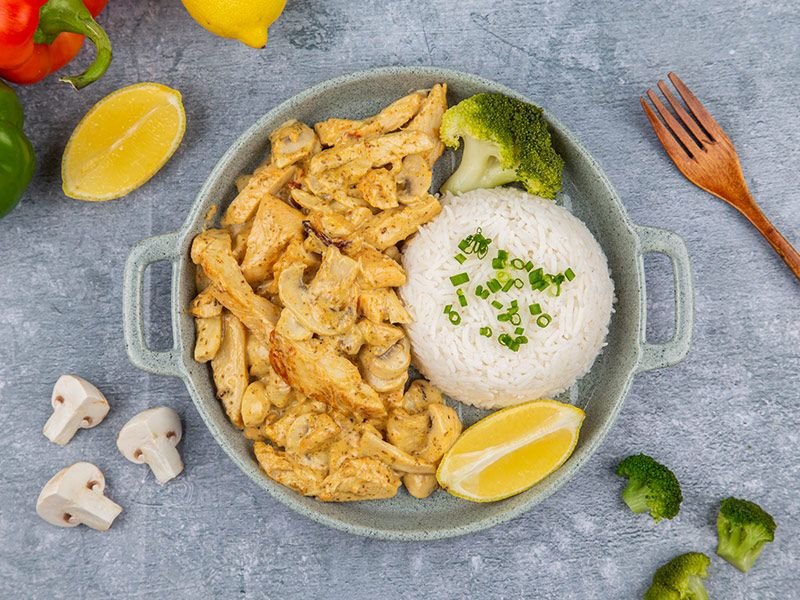
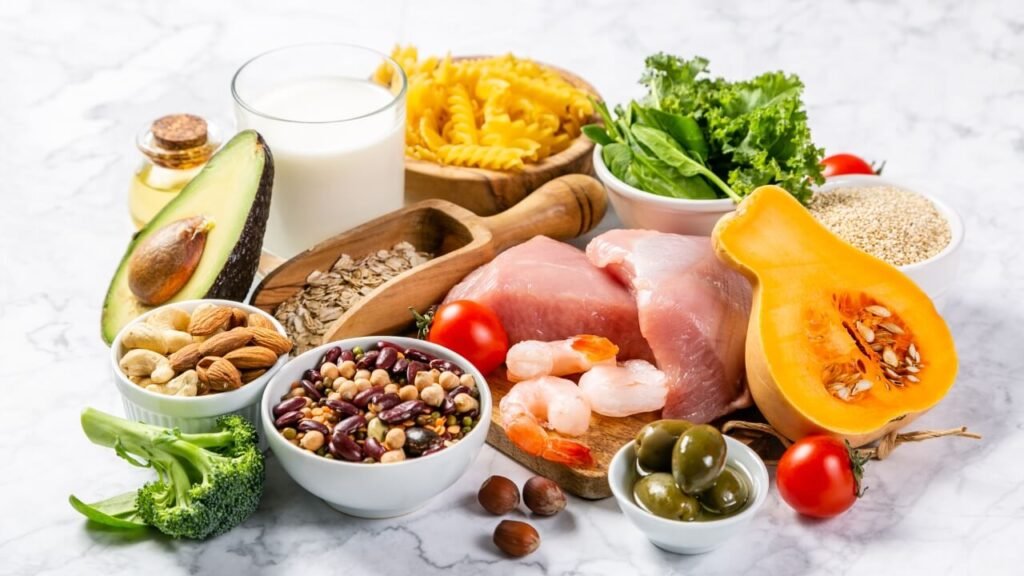
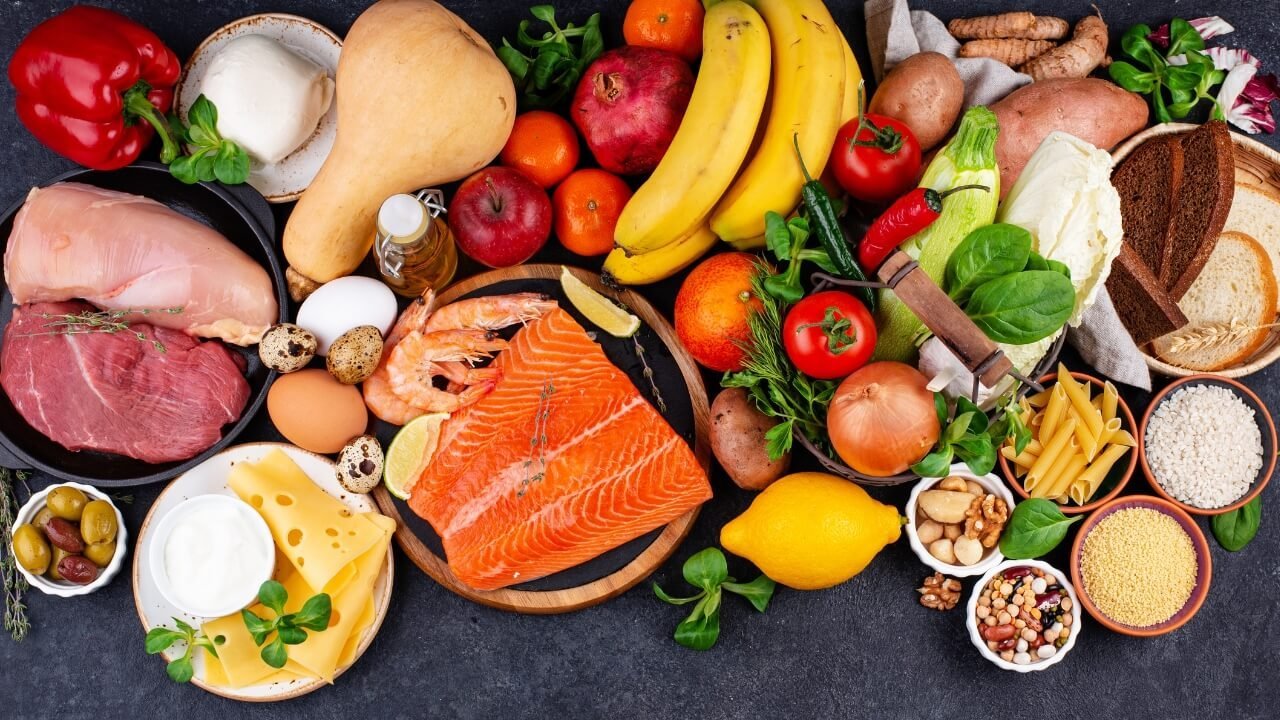
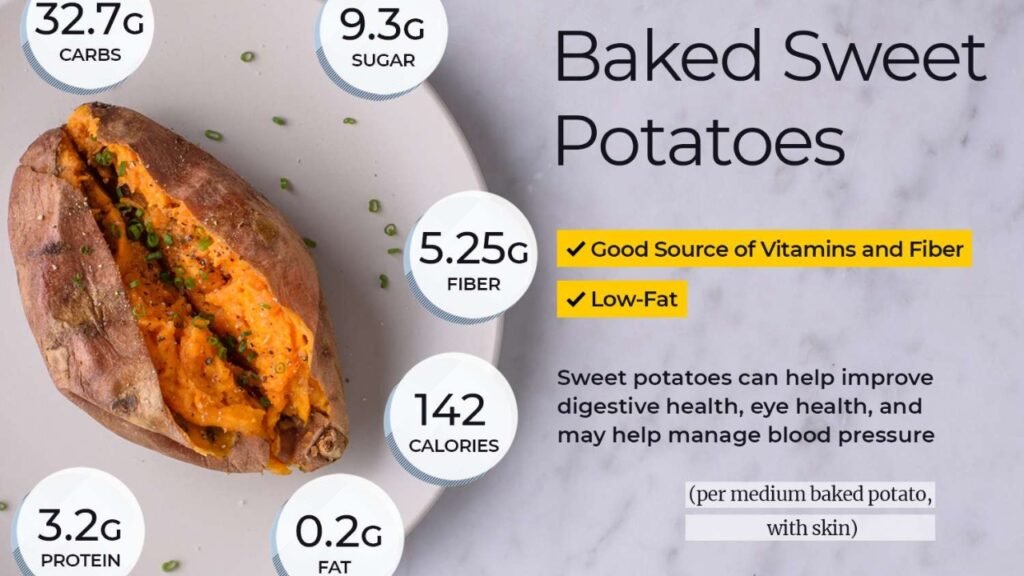
Carbohydrates form the foundation of the gastrointestinal soft diet food list because they are generally easy to digest and provide the body with energy. White rice, refined pasta, and white bread without seeds or nuts are excellent choices. These refined grains have had the bran and germ removed, which lowers their fiber content and reduces digestive strain. Additionally, starchy vegetables like potatoes (without skin) and squash cooked until soft fit perfectly into this diet.
While whole grains are typically encouraged for general health, during digestive distress, the fiber they contain can exacerbate symptoms. Therefore, it’s important to opt for low-fiber grains temporarily until the digestive system stabilizes.
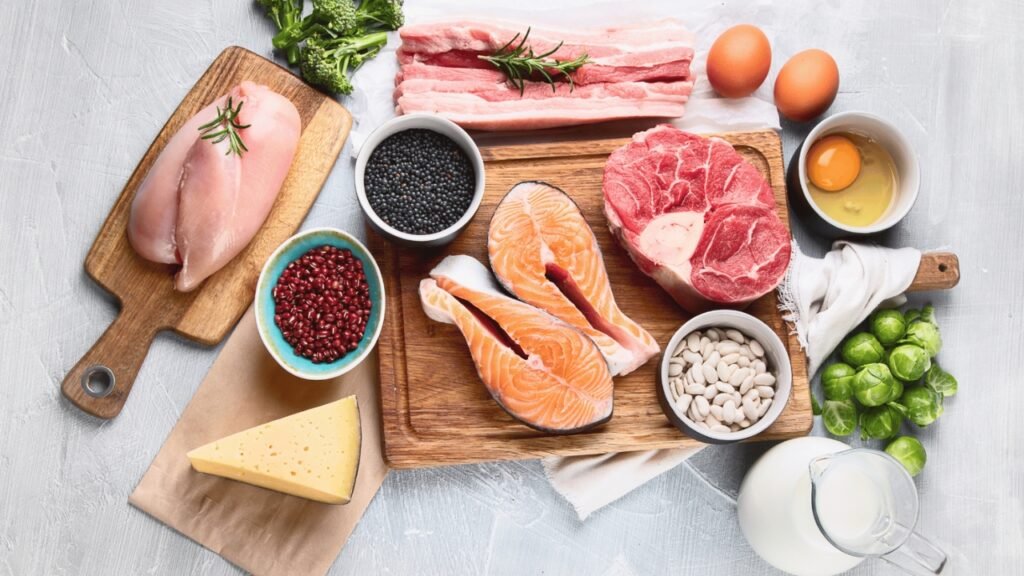
Proteins: Tender and Easily Digestible
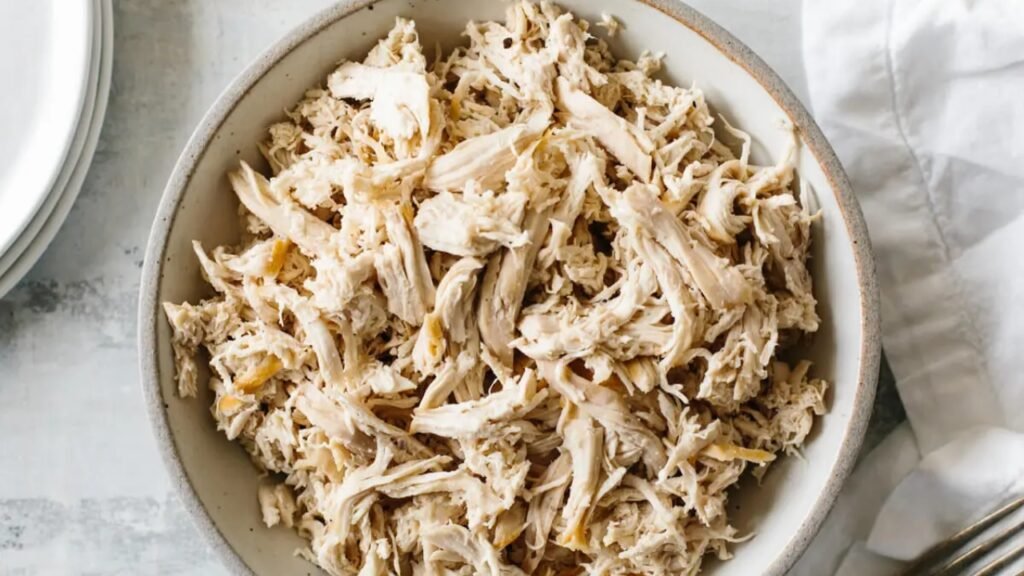
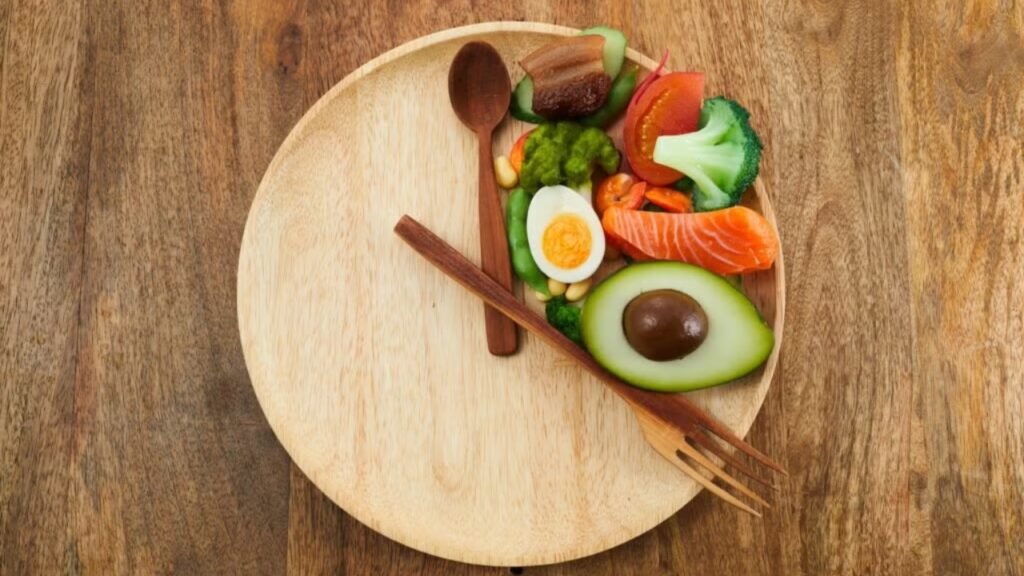
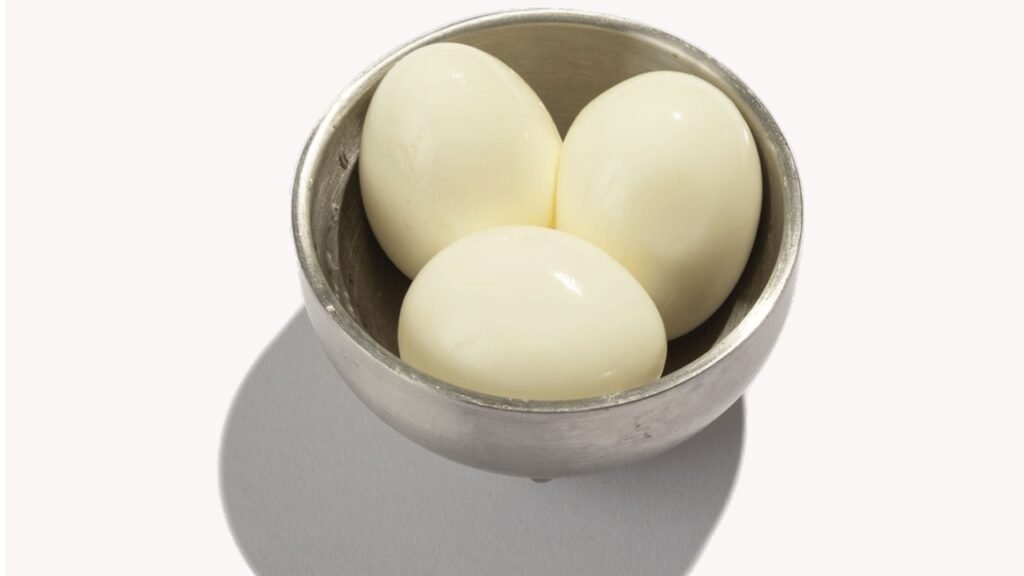
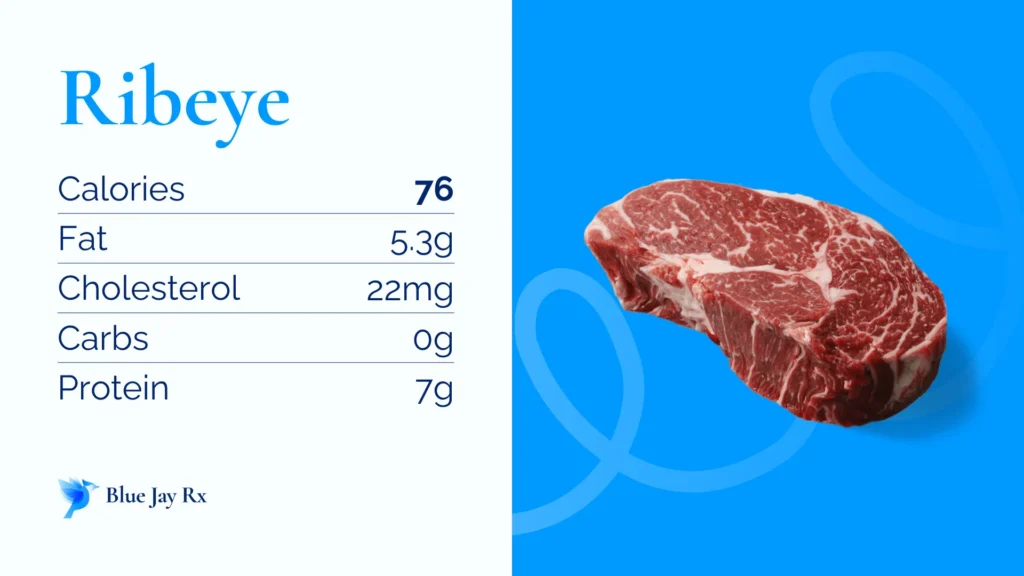
Proteins are essential for recovery and maintaining muscles, but tough cuts of meat can be difficult to digest. The gastrointestinal soft diet food list focuses on tender proteins such as ground chicken, turkey, and fish like cod or tilapia. Eggs, especially scrambled or poached, offer another gentle protein source.
Dairy products are allowed but only if they are tolerated well. Low-fat yogurt and cheese can be suitable options, but full-fat or heavily processed dairy might cause discomfort for some people, especially those who are lactose intolerant or have sensitive guts.
Fruits and Vegetables: Cooked and Peeled
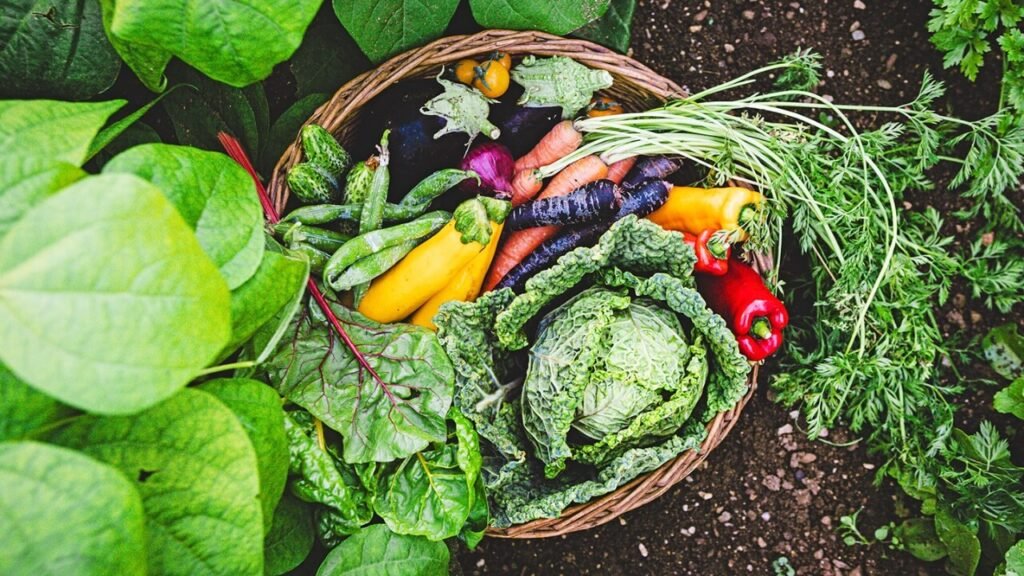
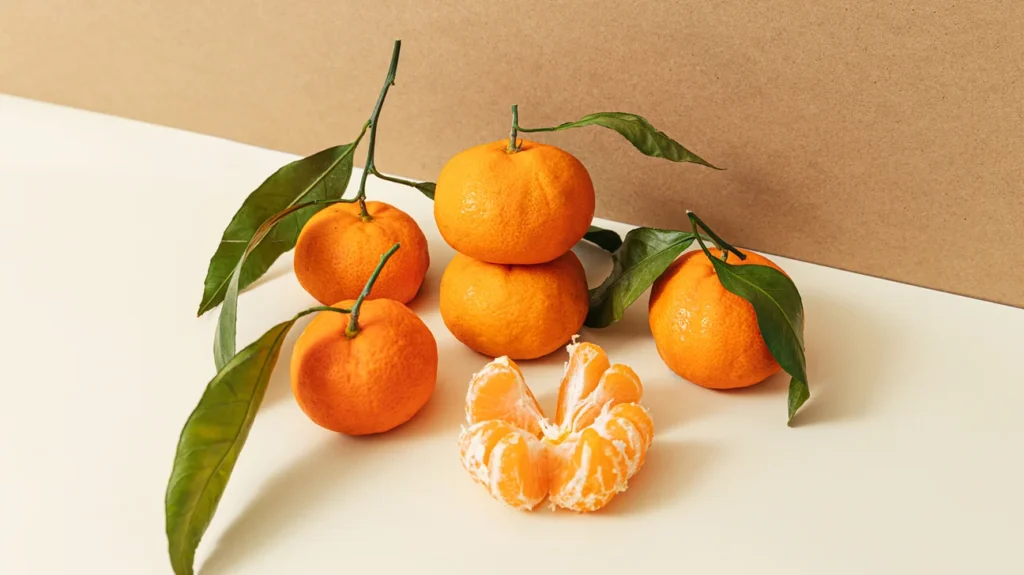
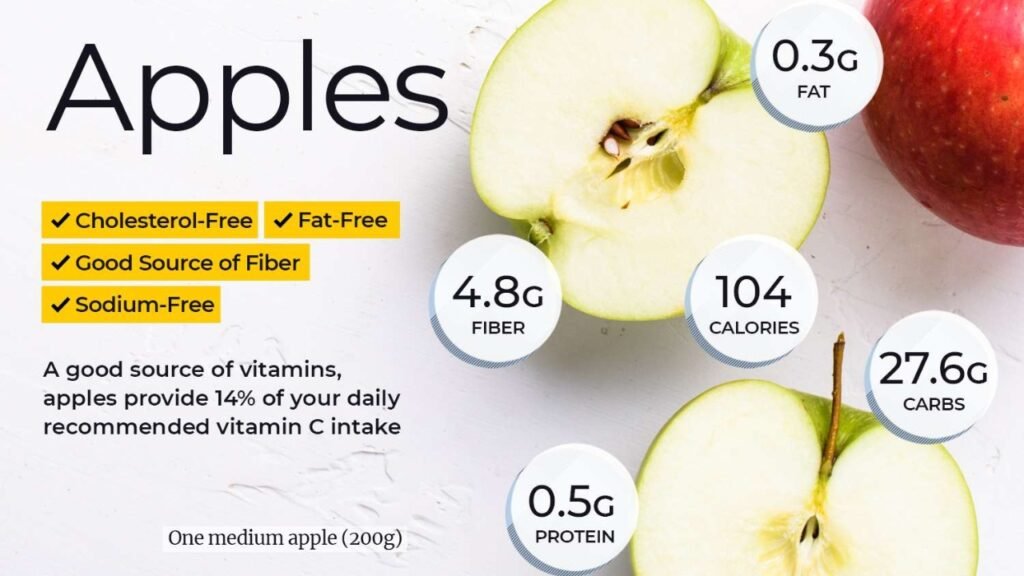
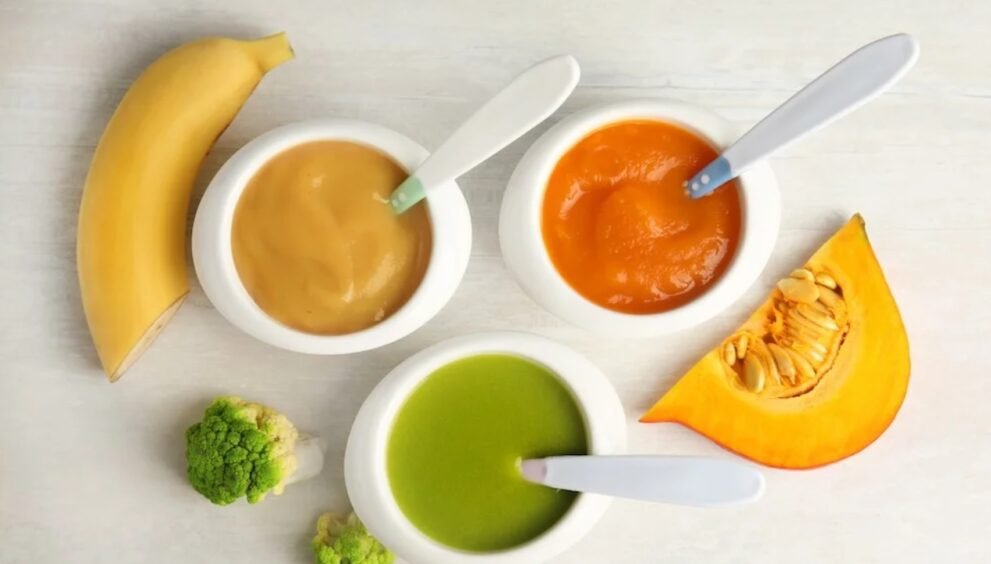
Raw fruits and vegetables often contain insoluble fiber and tough skins which can aggravate the digestive tract. Hence, the soft diet recommends consuming fruits and vegetables that are cooked, peeled, and soft. Applesauce, ripe bananas, cooked carrots, and peeled zucchini are commonly included in the diet.
Importantly, citrus fruits and tomatoes are generally avoided due to their acidity, which can worsen symptoms like heartburn or gastritis. Instead, mild and less acidic fruits like melons and peeled peaches provide nutritional benefits without triggering discomfort.
Fats: Minimal and Healthy
Although fats are necessary for overall health, fatty and fried foods are avoided because they slow digestion and can increase gastrointestinal symptoms. Healthy fats like small amounts of olive oil or avocado may be included but should be consumed sparingly.
The Role of Fluids and Beverages in a Soft Diet
Hydration is an often-overlooked part of managing gastrointestinal health. Clear broths, herbal teas, and diluted fruit juices without pulp are ideal beverages. These fluids keep the digestive system hydrated and help prevent constipation without causing irritation.
Caffeinated beverages, alcohol, and carbonated drinks are commonly discouraged as they can stimulate acid production and worsen symptoms. Water, in contrast, should be consumed regularly to aid digestion and nutrient absorption.
Scientific Insights on Soft Diets and Gastrointestinal Recovery
Research published in journals including Gastroenterology and The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition supports the efficacy of soft diets in managing gastrointestinal disorders. Studies emphasize that a low-residue diet, closely aligned with the gastrointestinal soft diet food list, can reduce bowel volume and frequency, allowing the gut to rest and heal.
One systematic review in Clinical Nutrition concluded that transitioning patients to a soft diet post-surgery decreased complications including nausea and abdominal pain compared to a regular diet, highlighting the importance of gradual dietary changes.
Moreover, recent research highlights the necessity of maintaining adequate protein and micronutrient intake during these phases to prevent muscle wasting and nutritional deficiencies, reinforcing the need for a well-balanced approach to the soft diet.
Common Challenges and Tips for Success
Following the gastrointestinal soft diet food list can sometimes feel restricting and monotonous. Many patients express concerns about lack of flavor and variety. However, creative cooking techniques, such as using herbs, mild spices, and broths, can enhance taste without irritating the gut.
Another challenge is ensuring adequate nutrition while restricting fiber-rich foods. Incorporating nutrient-dense soft foods like well-cooked legumes (if tolerated), smooth nut butters, and fortified dairy products can help maintain nutritional balance.
Additionally, portion control and frequent small meals support better digestion and prevent overwhelming the gastrointestinal tract.
Transitioning Back to a Regular Diet
The gastrointestinal soft diet is typically a temporary measure. As symptoms improve, patients can gradually reintroduce more complex and fiber-rich foods. This transition should be done cautiously, with attention to how the body responds to new foods.
A dietitian or gastroenterologist can provide personalized guidance during this phase, ensuring the diet remains supportive of digestive health while introducing variety and fiber for long-term wellness.
Conclusion: Embracing the Gastrointestinal Soft Diet Food List for Healing
In summary, the gastrointestinal soft diet food list offers a carefully crafted nutritional blueprint for anyone facing digestive challenges. By prioritizing easy-to-digest, low-fiber, and bland foods, this diet provides relief and supports the healing process. Though it requires adjustments and sometimes creativity, the benefits far outweigh the inconvenience.
Maintaining balance, consulting healthcare providers, and monitoring individual responses to foods are key to navigating this diet successfully. Ultimately, this approach empowers individuals to take control of their digestive health and improve quality of life during vulnerable periods.
“Understanding the nuances of what your digestive system needs can turn a difficult recovery into a manageable journey toward wellness.”
— Dr. Emily Watson
If you or a loved one are navigating gastrointestinal issues, embracing the soft diet food list with knowledge and care can make all the difference.
You May also read
Health Ade Kombucha Benefits: Unlock Surprising Wellness Secrets