Shoulder Pain: Stop Guessing, Start Healing! The Shoulder Pain Diagnosis Chart You NEED!
Shoulder pain is a common complaint, affecting millions of Americans each year. Finding reliable answers can feel like navigating a maze. When you’re struggling with limited mobility and constant discomfort, understanding the potential causes is crucial. This article serves as a comprehensive guide, using a shoulder pain diagnosis chart approach, to help you understand the possible origins of your pain and navigate the path toward effective treatment. We’ll explore a range of conditions, discuss diagnostic methods, and outline treatment options. So, let’s begin the journey towards relief and a pain-free future.
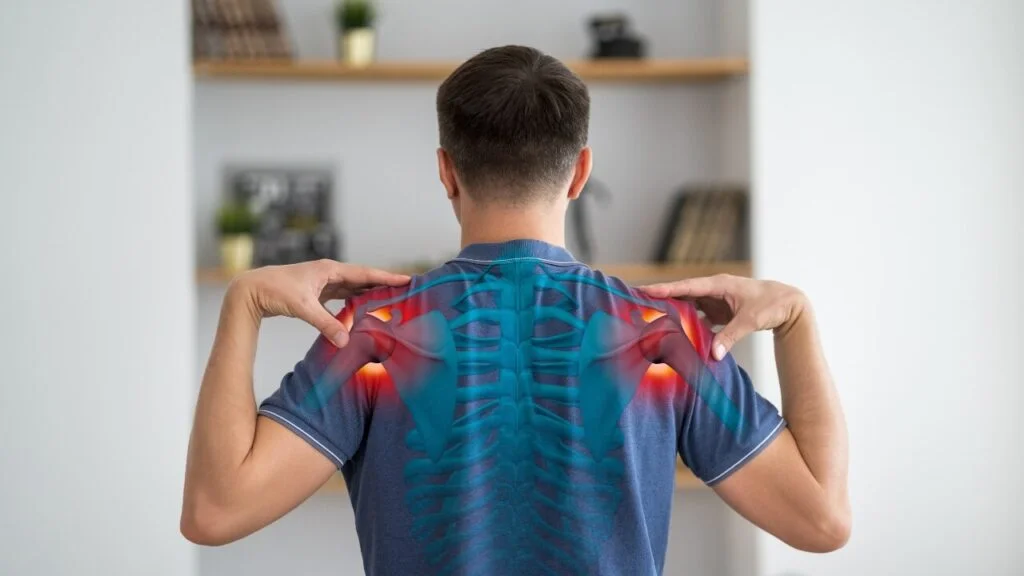
Understanding Shoulder Pain: A Complex Puzzle
The shoulder is a remarkable joint, boasting an incredible range of motion. However, this mobility comes at a cost: increased susceptibility to injury and pain. Because the shoulder involves a complex network of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones, pinpointing the exact cause of shoulder pain can be challenging. Moreover, pain felt in the shoulder might even originate from problems in the neck or upper back. This is called referred pain. Therefore, a thorough evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Common Causes of Shoulder Pain
Several factors can contribute to shoulder pain. These range from sudden injuries to chronic conditions that develop over time. The following sections delve into some of the most frequent culprits:
Rotator Cuff Injuries: The Overuse and Trauma Culprit
The rotator cuff, a group of four muscles and their tendons, stabilizes the shoulder joint and enables a wide range of arm movements. These injuries are a very common cause of shoulder pain. Damage to these tendons and muscles can occur due to repetitive overhead activities, such as painting, throwing, or swimming. Furthermore, acute injuries, such as falls or direct blows to the shoulder, can also tear the rotator cuff. In addition, consider that age and previous injuries can predispose an individual to rotator cuff tears.
- Symptoms: Rotator cuff injuries often manifest as a dull ache deep within the shoulder. Additionally, you might experience pain when lifting or rotating your arm. Night pain, especially when lying on the affected side, is also a frequent complaint. Weakness in the arm is common.
- Diagnosis: Doctors typically diagnose rotator cuff injuries through physical examination and imaging tests. These include X-rays, which can rule out bone problems, and MRI scans, which can visualize the soft tissues, such as the tendons and muscles of the rotator cuff.
- Treatment: Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the tear. Conservative measures, such as rest, ice, physical therapy, and pain medication, are often the first line of defense. However, for severe tears, surgery might be necessary to repair the damaged tendons. Reddit users frequently discuss their experiences with rotator cuff repair surgery, providing insights into the recovery process.
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: When Space Becomes Limited
Shoulder impingement syndrome occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff become compressed as they pass through a narrow space beneath the acromion (part of the shoulder blade). This compression can lead to inflammation and pain. Bone spurs, thickening of the bursa, or variations in the acromion’s shape can contribute to the narrowing of this space.
- Symptoms: Pain is often felt on the outside of the shoulder and may radiate down the arm. It is also common for pain to worsen with overhead activities and reaching behind the back. You might also feel a catching sensation or clicking in the shoulder.
- Diagnosis: Physical examination, including specific impingement tests, is a key part of the diagnosis. X-rays can reveal bone spurs, while MRI scans can assess the rotator cuff tendons and bursa.
- Treatment: Initial treatment typically involves rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications. Physical therapy focuses on strengthening the rotator cuff muscles and improving shoulder mechanics. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation. Surgery, such as arthroscopic acromioplasty (removing part of the acromion), may be considered if conservative treatments fail.
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis): A Gradual Loss of Motion
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint. It occurs when the capsule surrounding the shoulder joint thickens and tightens, restricting movement. This can be incredibly debilitating. The exact cause of frozen shoulder is unknown, but it’s more common in people with diabetes, thyroid disorders, and those who have recently experienced a shoulder injury or surgery. It is essential to start treatment early.
- Symptoms: Frozen shoulder typically progresses through three stages: a painful freezing stage, a frozen stage with significant stiffness but less pain, and a thawing stage with gradual return of motion.
- Diagnosis: The diagnosis is primarily based on physical examination and the patient’s history. X-rays are usually normal, but an MRI might be performed to rule out other conditions.
- Treatment: Treatment aims to relieve pain and restore range of motion. Physical therapy is crucial, focusing on stretching exercises and joint mobilization techniques. Pain relievers and corticosteroid injections can help manage pain. In severe cases, surgery might be recommended to release the tightened joint capsule.
Shoulder Bursitis: Inflammation of the Cushions
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones, tendons, and muscles around the shoulder joint. Bursitis occurs when these bursae become inflamed, often due to repetitive motions or overuse. It is common for someone with bursitis to experience reduced ROM.
- Symptoms: Shoulder bursitis causes pain, stiffness, and tenderness around the shoulder joint. The pain may worsen with activity and be especially noticeable when raising your arm overhead.
- Diagnosis: A doctor will assess your symptoms and conduct a physical examination to determine if you have bursitis. In some cases, imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, may be used to rule out other conditions.
- Treatment: Treatment for shoulder bursitis typically includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Additionally, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy can also be beneficial to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve range of motion. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be necessary to reduce inflammation.
Osteoarthritis: The Wear-and-Tear Culprit
Osteoarthritis, also known as wear-and-tear arthritis, can affect the shoulder joint. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones gradually breaks down. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. This is often a long-term concern.
- Symptoms: Pain is often the primary symptom, and it can worsen with activity. Stiffness, especially in the morning, is also common. As the condition progresses, you might hear a grinding sensation (crepitus) in the shoulder joint.
- Diagnosis: X-rays are the primary diagnostic tool, revealing narrowing of the joint space, bone spurs, and other signs of cartilage degeneration.
- Treatment: There is no cure for osteoarthritis, so treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving function. Physical therapy, pain relievers, and lifestyle modifications, such as weight management, can help. Corticosteroid injections can provide temporary relief. In severe cases, shoulder replacement surgery might be considered.
Shoulder Pain Diagnosis Chart: A Visual Aid for Understanding
A shoulder pain diagnosis chart can be a helpful tool for narrowing down the potential causes of your shoulder pain. These charts typically organize common shoulder conditions based on symptoms, location of pain, and aggravating factors. It can serve as a starting point for self-assessment, but it should not replace a professional medical evaluation. Remember, accurate diagnosis requires a thorough examination by a healthcare provider.
Utilizing a Shoulder Pain Chart Effectively
Here’s how you can use a shoulder pain diagnosis chart effectively:
- Identify Your Symptoms: Note the specific characteristics of your pain. Is it sharp, dull, aching, or burning? Where is the pain located? Does it radiate down your arm or into your neck?
- Determine Aggravating Factors: What activities make your pain worse? Overhead movements, reaching behind your back, or sleeping on your side?
- Consider Your Medical History: Do you have any underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or thyroid problems? Have you recently experienced a shoulder injury?
- Consult the Chart: Once you have gathered this information, consult the shoulder pain diagnosis chart. Compare your symptoms and aggravating factors to the conditions listed.
- Seek Professional Evaluation: It’s crucial to remember that a shoulder pain diagnosis chart is only a guide. You should consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Expert Insight on Shoulder Pain Diagnosis
“The shoulder is a complex joint, and accurately diagnosing the source of pain requires a thorough evaluation,”
says Dr. Michael J. Lee, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in shoulder and elbow conditions.
“Patients often try to self-diagnose based on online information, which can be misleading. A proper physical exam, along with appropriate imaging studies, is essential for determining the underlying cause of the pain and developing an effective treatment strategy.”
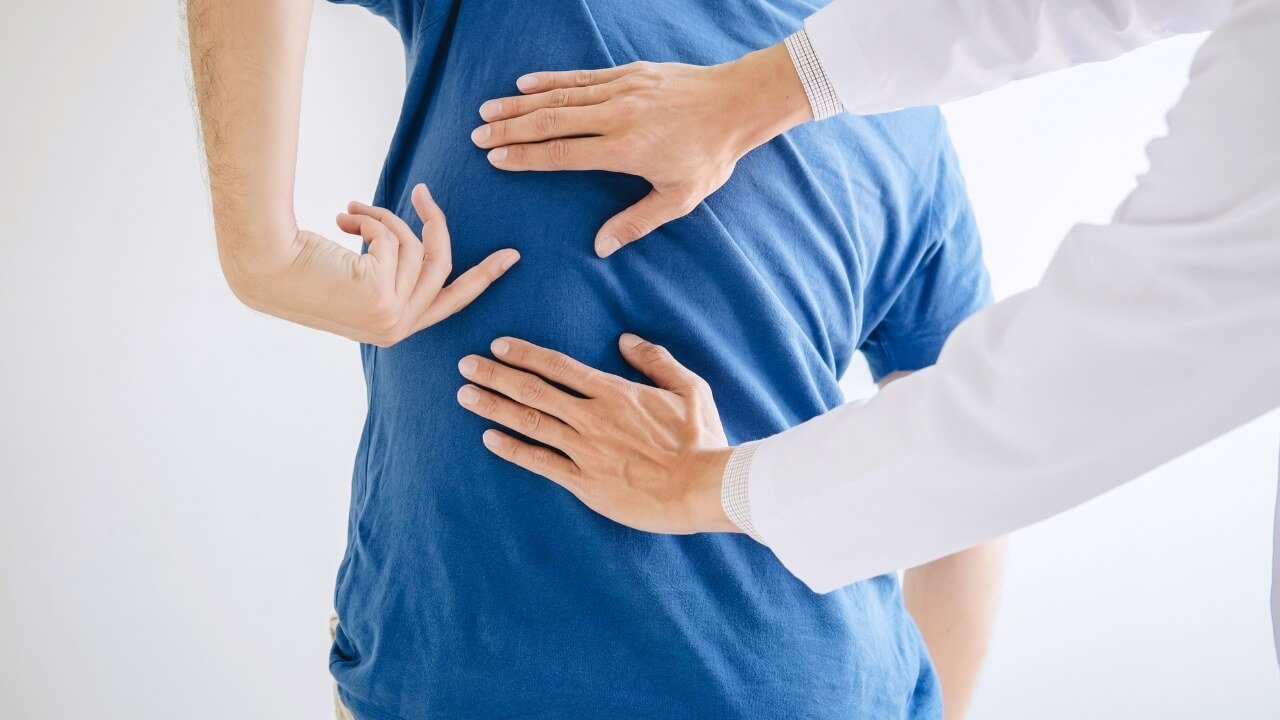
The Importance of a Comprehensive Evaluation
While a shoulder pain diagnosis chart can be helpful in providing some preliminary information, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
What to Expect During a Shoulder Evaluation
During a shoulder evaluation, your doctor will:
- Review Your Medical History: They will ask about your past medical conditions, medications, and any previous shoulder injuries or surgeries.
- Perform a Physical Examination: They will assess your range of motion, strength, and reflexes. They will also perform specific tests to evaluate the stability of your shoulder joint and identify any areas of tenderness.
- Order Imaging Tests: Depending on the findings of the physical examination, your doctor may order imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasound, to further evaluate your shoulder joint.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Pain
The treatment for shoulder pain will vary depending on the underlying cause. However, some common treatment options include:
Conservative Treatment:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate your pain.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Compression: Using a compression bandage to reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Keeping your shoulder elevated to reduce swelling.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications to manage pain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches to improve range of motion, strength, and stability.
Injections:
- Corticosteroid Injections: To reduce inflammation and pain.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: To lubricate the joint and reduce friction.
Surgery:
- In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged tissues, such as torn rotator cuff tendons or ligaments.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Shoulder Health
Shoulder pain can significantly impact your quality of life, limiting your ability to perform everyday activities. However, with a thorough understanding of the potential causes and the importance of seeking professional medical evaluation, you can take control of your shoulder health and find relief. While a shoulder pain diagnosis chart can provide a starting point for understanding your symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Remember to focus on proactive measures such as proper posture, ergonomic work habits, and regular exercise to prevent future shoulder problems. Ultimately, understanding your body and seeking timely care are the keys to managing shoulder pain effectively and enjoying a pain-free, active lifestyle.
Unlock Ageless Movement: Classical Stretch Secrets the Fitness Industry Doesn’t Want You to Know!