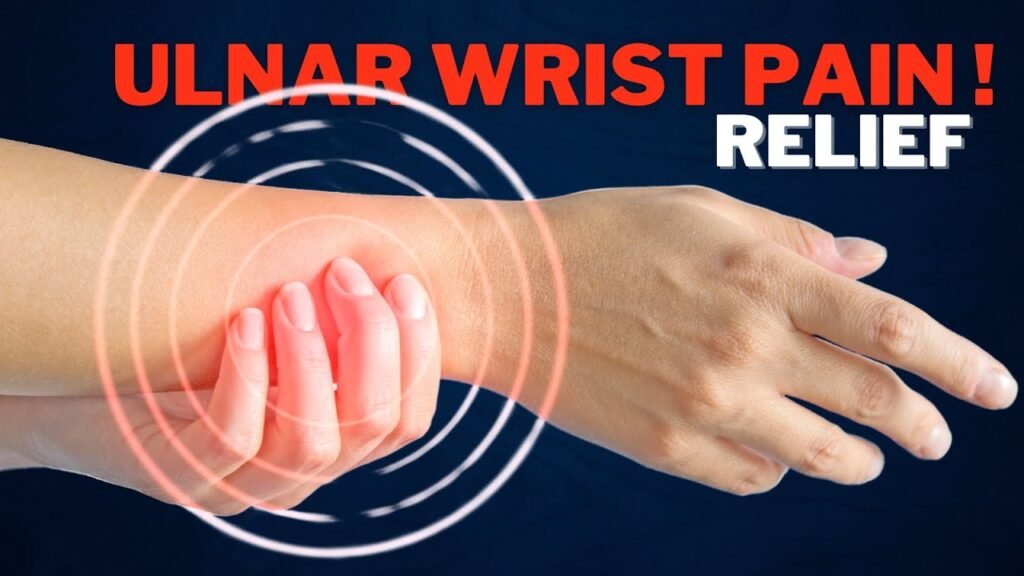
Ulnar Wrist Pain Treatment: End Pain Quickly!
Ulnar wrist pain treatment is vital for people experiencing soreness and restricted mobility at the little finger side of their wrist. Whether you are an athlete, a workplace worker, or simply experiencing aging-related joint wear, knowing how to effectively treat ulnar wrist pain can greatly improve your quality of life. This complete guide explores the best practices, treatment options, and preventive measures to control and alleviate ulnar wrist pain.
Common Causes and Symptoms
Ulnar wrist pain commonly originates from injuries or repetitive strain on the ulnar side—the pinky finger side—of your wrist. This pain can be sharp, dull, persistent, or intermittent, impacting everyday tasks like typing, lifting, or even basic movements. Common causes include ulnar impaction syndrome, triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) injuries, arthritis, or fractures.
Dr. James Bennett, a leading orthopedic surgeon, states,
“Early diagnosis and targeted treatment of ulnar wrist pain can dramatically enhance recovery outcomes, preventing further complications.”
Recognizing symptoms early on—such as swelling, clicking or popping sensations, stiffness, or reduced grip strength—allows you to seek timely treatment, significantly improving prognosis.
Diagnosis of Ulnar Wrist Pain
Effective ulnar wrist pain treatment starts with accurate diagnosis. Healthcare providers typically begin with a detailed physical examination, assessing pain levels, mobility, and swelling. Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound may also follow to identify underlying issues such as ligament tears, fractures, or degenerative conditions.
A detailed medical history discussion, including occupation, activities, and previous wrist injuries, is equally essential for pinpointing the exact cause. Comprehensive diagnostics ensure a targeted and effective treatment strategy.
Non-Surgical Ulnar Wrist Pain Treatment
Before considering invasive procedures, healthcare professionals typically recommend conservative treatment methods. These approaches aim to reduce inflammation, promote healing, and restore wrist functionality.
Rest and Activity Modification
Initially, it’s crucial to rest your wrist and avoid activities causing strain. Modifying daily tasks, such as taking breaks during repetitive movements or using ergonomic tools, significantly reduces strain. Wrist braces or splints might be recommended to immobilize and support the area, helping tissues heal effectively.
Medication
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen or naproxen, are commonly prescribed for pain relief and inflammation reduction. Topical creams and gels may also provide localized relief.
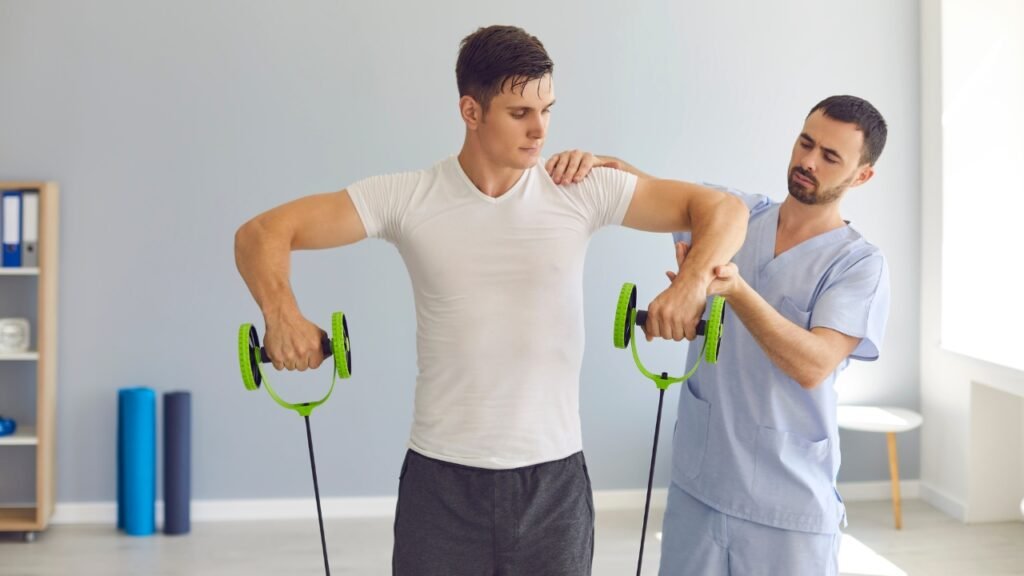
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is pivotal in rehabilitating the wrist. Therapists guide patients through specific exercises that strengthen the wrist and forearm muscles, enhancing stability and flexibility. Customized routines often include stretching, strengthening, and mobility exercises, significantly alleviating discomfort and improving function.
Advanced Treatments for Ulnar Wrist Pain
If conservative treatments fail to deliver sufficient relief, advanced interventions may become necessary.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections directly into the wrist area can provide immediate, substantial relief from inflammation and pain. This treatment option is especially effective for acute flare-ups of pain or inflammation.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy uses injections of a concentration of a patient’s own platelets to accelerate the healing of injured tendons, ligaments, muscles, and joints. Clinical studies published in orthopedic journals indicate promising results for chronic ulnar wrist pain cases resistant to traditional treatments.
Surgical Treatment for Persistent Ulnar Wrist Pain
When conservative methods are insufficient, surgical intervention may become necessary. Surgery aims to repair damage, relieve compression, or reconstruct damaged tissue.
Arthroscopic Surgery
Minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery involves inserting tiny instruments through small incisions. It effectively addresses TFCC tears or minor ligament injuries, offering reduced recovery times and minimal scarring.
Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy
In cases of ulnar impaction syndrome, an ulnar shortening osteotomy—a procedure that shortens the ulna bone—can significantly alleviate pain by reducing pressure on the wrist’s ulnar side.
Preventing Ulnar Wrist Pain
Preventive measures are vital for minimizing the risk of recurrence or onset of ulnar wrist pain. Incorporating regular wrist exercises into your routine strengthens the muscles supporting your wrist. Ergonomic tools and proper wrist positioning during repetitive tasks reduce the likelihood of injury.
Additionally, maintaining overall wrist health through balanced nutrition and hydration supports joint and ligament integrity, enhancing resilience against injuries.
When to Seek Professional Help
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if your wrist pain persists beyond a few days, intensifies despite home remedies, or significantly impairs daily activities. Timely professional intervention dramatically improves treatment outcomes and prevents chronic complications.
Concluding Thoughts
Effective ulnar wrist pain treatment involves a multifaceted approach tailored to individual needs. From conservative home care and medications to advanced medical interventions and preventive practices, managing ulnar wrist pain is achievable with professional guidance and proactive self-care. Remember, early intervention not only provides relief but also safeguards against long-term wrist dysfunction, ensuring a better quality of life.