The Russian Squat: How to master an Ancient Strength Building Technique
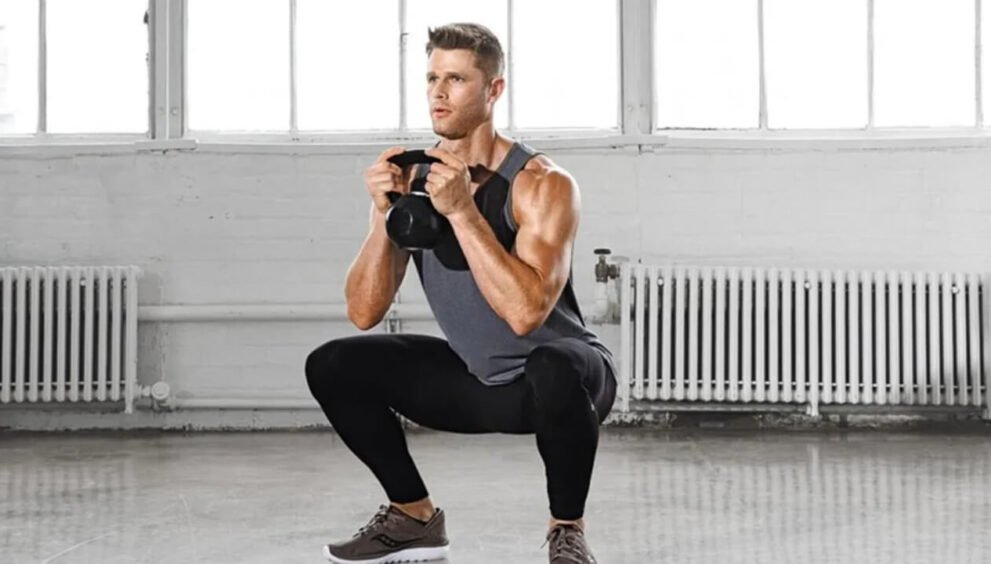

When it comes to legendary strength building tactics, chances are most of the people will think directly towards Russian squat as a mixture of culture, sporting skills, and brute power. Out in the strength training world, the Russian squat is not simply a leg exercise-it is a philosophy based in precision, discipline and progressive overload. This type of training has gained popularity among the best athletes, power lifters and sport professionals all over the world due to its effect on lower body strength, explosive power as well as upgrading the performance of an athlete. In the US, the Russian squat has rapidly gained interest as fitness fanatics in the US search out tested, science-supported means of overcoming the plateau and engaging in optimal performances.
The origin of the Russian squat dates to Soviet era sports science in which careful programming and following it with precision visual questions gave the lifter options to set personal and world marks. Now the great thing about this program is that it is as appropriate as it has ever been to the people who desire not only to have stronger legs but also have a organized way to quantitatively improve.
History and origins of the Russian squat
The Russian squat was a by-product of the Soviet systematic training of athletic performance in the middle-to-late 20 th century. Sport performance was of national interest during those times, and it was through the thorough biological intervention of mathematicians, scientists and medical experts such as biomechanics, periodization and recovery modalities that training programs were prepared that achieved maximum results. Russian squat program was notorious among Olympic lifters and power athletes as it delivered results not only once but repeatedly.
The Russian squat scheme differed with random training schemes as it was strategized to intensely overload the muscles in a rigid six-week session with both heavy days and lighter days aimed at increased neuromuscular efficiency. Soviet coaches viewed it as a manner of conditioning athletes to make record breaking lifts and not burning them out a manner that has since been proven through the science of modern sporting.
Science of the Russian Squat
The Russian squat is built on the basis of periodization- a specific system of training in which the volume and intensity of the training is alternated in a planned manner during a specific time frame. It makes sure that the body gets adapted but does not need to over train.
Traditionally it takes about six weeks to complete a Russian cycle of squats, consisting of 3 squat sessions each week:
- One heavy day of maximal strength.
- Speed/tehchnique one of the light days.
- One volume and control day.
The concept is straight forward: progressively gage your muscles by performing weight that challenges the muscle during the exercise, but allow the muscle sufficient recovery to build and develop. This exercise builds quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, lower back and core strength, however, the program also incorporates development of tendons, ligaments and stabilizing muscles.
The contemporary exercise physiology endorses this strategy. Training should be exact, as was once mentioned by Dr. Yuri Verkhoshansky, a highly decorated scientist of soviet sport. The body will undergo a very specific kind of adaptation to demands conducted on it and an ideal example of specific adaptation is the Russian squat.”
Russians Squat Properly: Cueing the Russian Squat Properly
Although the Russian squat program can be referred to as a system, the squat itself technique is also significant. The wrong usage would not only make it less effective, but could also pose more danger to injury.
- Positioned under barbell: Your feet should be shoulder-width apart; with your toes turned out a bit.
- Tighten your stomach: Use abdominal muscles to your support spine.
- Control in descent: Straighten the torso by bending the knees and the hips at the same time, lower yourself at least until they are parallel to the ground, or below (as you can, of course).
- Power off: Power off forward and out with your heels and midfoot in the air and the chest up and returning to the beginning position.
High-bar squat position is also the choice of many athletes in Russian squat program because it is the best position to develop quads and maintain an upright position. But a low-bar positioning may also be applied to those who give more attention to powerlifting objectives.
Romanian Deadlift Benefits
1. Lack of lower-body strength
Russian squat places high frequency, progressive loads on the body which requires adaptation to quick adjustment. Increases in one-rep max during a complete cycle are commonly 5 10% by lifters who report such gains.
2. Improved Explosiveness
Since the program consists of developing speed and medium-intensity days, the athletes end up having not only developing raw strength but wearing it fast, which is also an essential component in athletic access such as football, wrestling, and basketball.
3. Mental Toughness
The regime of the Russian squat is rigid and needs discipline. This not only develops physical strength, but also cultivates inner strength and mental fortitude as lifters continue to work into the fatigue to eke out heavy sets.
4. Improved Muscle Strength Essential Muscle Endurance
The volume of the program trains muscles to do more work as time goes by, equating to better performance on other lifts and during sports play.
The Mistakes to Avoid the Russian Squat
- The Russian squat is very effective but hard and without proper performance will result in an injury or burnout. The temptations to follow include:
- Missed recovery days: Recovery days are a part of the program, not to be done on the whims- without it progress is doomed.
- Poor form when under a load/fatigued: It is essential to learn to keep proper mechanics of squat during the weeks.
- Jumping in too heavy: You should start doing the program using a realistic training max; if you overestimate it will lead to a halt in progress.
Russian Squat vs. Other Squat Programs
In comparison to other squat programs that are as popular as Smolov or 5×5, the Russian squat offers a well balanced zone between hard and rest. As an example, Smolov is notorious in its brutality and will in most cases result in overtraining by non-elite athletes. Comparatively however, Russian squat uses a measured progression that only makes it sustainable to a wider population of lifters yet still achieves remarkable results.
The next similarity is with the Texas Method as this training method also involves the use of volume and intensity days, which are used more widely on full body training. Russian squat is very special, consisting of the squat isolation training only.
Russian Squat adjusted to American Sportsmen
The American gym culture tends toward variety, again, mixing up the exercises performed so as to shock the muscles. Though variety certainly has advantages, the Russian squat shows that specific repetition with delivered overloading can be even more productive when it comes to gaining raw strength.
To American athletes:
- The program will allow powerlifters to peak in preparation to compete.
- It can be used in the off-season CrossFit training of strength during the legs.
- Athlete of a team sport can do modified forms to maintain during the season.
Theory behind the Russian Squat
In order to get a better idea of why it has been so popular, I got in touch with Mark Rippetoe, a strength coach and the author of Starting Strength. He does not restrict his attention to the Russian methods alone, but he approves their utility, when he says:
Russian squat cycle is intelligent disciplined programming. It is not snazzy but it performs. Whoever is prepared to do it will get verifiable repeatable outcomes.”
This underlines the point that real improvement is the result of strategic, steady work and the concept of random, intensive fads.
Sample 6 Weeks Russian Squat Cycle
This is a simplified demonstration of how the program can appear, depending on a lifter current-one-rep max (1RM):
Week 1
- Day 1: 1RM x 80% 6 sets x 2 reps
- Day 2: 6 rep max Deload- 6 sets x 2 reps ( velocity )
- Day 3: 80 percent of 1RM 3 sets x6 reps
The percentages and rep schemes start out small each week, then build progressively up to Week 6 in which the lifter tries a new max.
The Russian Squat and Recovery and Nutrition
- Due to the high rate and intensity, the recovery plans are vital:
- Sleep: 8+ hours a night.
- Nutrition: Stay in caloric surplus with sufficient protein (1.6-2.2g of protein in each kilogram of body weight).
- Mobility work: Use stretching exercises and foam rolling to avoid becoming stiff.
- Active recovery: Low-intensity cardiopulmonary activities such as swimming may increase blood flow and help recovery.
Reasons Why the Russian Squat Is a Sound Choice in the Modern World In Final Thoughts
Russian squat is not just a training, it is about power of structure, discipline, and gradual development. This program provides a blueprint towards strength development that has proven to work in case American athletes are tired of following the musical approach towards strength development. It instills the values of patience, helps develop the mental strength and offers long term results.
The Russian squat is a time proven way to achieve your squat goals as a lifter, competitive athlete, or simply being who you want to be in terms of being able to squat more than you ever have. Overall, its history of Soviet sports science to the present American gymnasium proves that where power is concerned, specificity will always win over randomness.