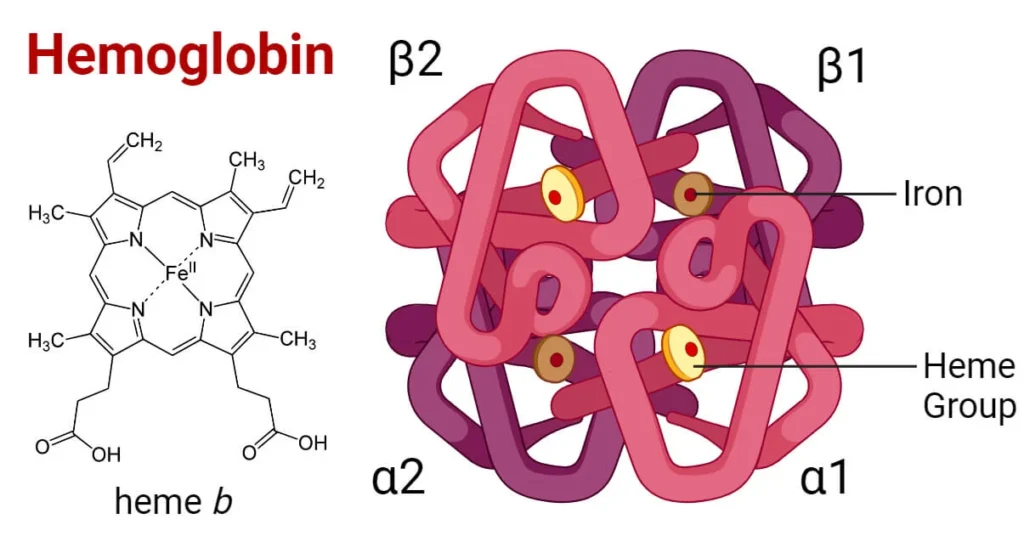
Why Russet Potatoes Nutrition Deserves a Closer Look

Russet potatoes are a staple in infinite American kitchens, gracing dinner plates inside the form of baked potatoes, mashed sides, crispy fries, and more. While often associated with comfort food, the russet potatoes nutrition profile reveals a surprising array of health benefits that go far beyond their reputation as starchy carbs. When consumed mindfully and prepared well, russet potatoes can play a valuable role in a balanced diet.
With an increased focus on whole foods and plant-based eating, it is time to re-evaluate the humble russet potato—not only for its versatility and flavor, but for the nutrients it provides. Let’s dig deeper into the world of russet potatoes nutrition, examining how this common crop contributes to our health and well-being, with insights supported by scientific studies and expert opinion.
The Nutritional Powerhouse Inside a Russet Potato
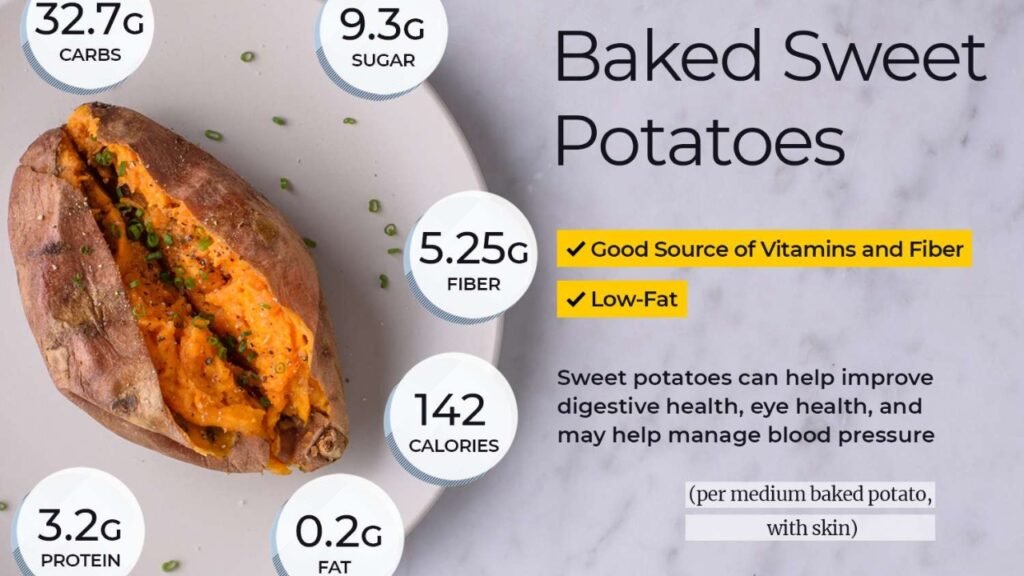
A medium-sized russet potato (approximately 173 grams) with the skin on contains around 168 calories, most of which come from carbohydrates. However, unlike refined carbs found in processed foods, russet potatoes deliver complex carbohydrates, which digest more slowly and provide sustained energy. They contain about 37 grams of carbs, 4 grams of protein, and virtually no fat. The **fiber content—roughly 3 grams—**mostly comes from the skin, making it an essential part of the potato’s dietary value.
According to a 2020 publication in Nutrients, complex carbs like those in potatoes help maintain blood glucose balance and can enhance satiety, potentially aiding in weight control when part of a balanced meal [1].
Vitamins and Minerals Galore
Russet potatoes offer an impressive range of essential vitamins and minerals. They are especially rich in potassium—offering more than 900 mg per serving—which supports healthy muscle function and blood pressure regulation. This makes them a preferred source of potassium even over bananas.
They also contain a generous dose of vitamin C, with a single russet potato providing around 14% of the daily recommended intake. Additionally, they provide vitamin B6, folate, iron, magnesium, and small amounts of zinc and calcium. These nutrients play vital roles in everything from energy production to immune support.
As Dr. Karen Collins, MS, RDN, explains,
“Potatoes—especially when eaten with their skins—provide nutrients that support immune function and heart health, and they’re naturally free of cholesterol and sodium.” [2]
Health Benefits of Russet Potatoes
The russet potatoes nutrition profile is particularly heart-friendly. The high potassium content helps to counteract the effects of sodium, which is beneficial for people managing hypertension. Additionally, their fiber helps reduce bad cholesterol (LDL), thereby promoting cardiovascular well-being.
The American Heart Association recognizes potassium-rich foods as part of a heart-healthy diet. Moreover, when russet potatoes are prepared without heavy creams, butter, or deep-frying oils, they serve as a low-fat, heart-supportive option.
Digestive Wellness and Gut Health
Fiber is essential for maintaining healthy digestion, and russet potatoes—particularly when eaten with the skin—provide both soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber helps regulate blood sugar and lower cholesterol, while insoluble fiber promotes bowel regularity and gut motility.
Scientific literature, including a study from Frontiers in Nutrition (2019), suggests that dietary fiber also contributes to a healthy gut microbiome, which influences immunity and even mood regulation [3].
Blood Sugar Management
While potatoes have a high glycemic index (GI), their glycemic load (GL) can be moderated by preparation methods and portion control. For example, allowing boiled potatoes to cool increases their resistant starch content, which lowers their glycemic impact.
According to research published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, resistant starch improves insulin sensitivity and enhances satiety, making it easier to manage hunger and energy levels throughout the day [4].
Cooking Methods Matter: Healthy Ways to Enjoy Russet Potatoes
The way you prepare russet potatoes can significantly affect their nutritional profile. Baking, boiling, or steaming potatoes with the skin intact is the healthiest approach, as it retains fiber and minimizes nutrient loss. Avoid deep-frying or heavily buttering, which adds empty calories and unhealthy fats.
Steaming with herbs or baking with olive oil and spices can make for a delicious and wholesome side dish that enhances both flavor and russet potatoes nutrition.
Pairing for a Balanced Plate
To make the most of russet potatoes, pair them with lean proteins like grilled chicken, legumes, or fish, along with green vegetables for added fiber and micronutrients. This ensures your meal contains a variety of food groups, balances blood sugar, and maximizes satiety.
When russet potatoes are part of a well-rounded meal, they become far more than a filler—they transform into a nutritional asset.
Common Myths About Russet Potatoes—Debunked
Weight gain is not about any single food but rather overall calorie intake and activity level. Russet potatoes are naturally low in fat and high in nutrients. Overeating fried or butter-heavy versions contributes to weight issues, not the potato itself.
Myth 2: Potatoes Are “Empty Carbs”
This myth stems from lumping russet potatoes with white bread or sugary cereals. In contrast, russet potatoes contain essential nutrients and complex carbohydrates that fuel the body efficiently. In fact, the russet potatoes nutrition value makes them a smart choice for athletes and active individuals.
Russet Potatoes vs. Other Potato Varieties
Russet potatoes are often compared to red, Yukon gold, or sweet potatoes. While sweet potatoes contain more vitamin A due to beta-carotene, russets provide more iron and are lower in sugar. Each type has its strengths, but russets remain unmatched in their fluffiness and suitability for baking and mashing.
Their higher starch content makes them ideal for certain recipes, and when prepared healthfully, they remain a nutrient-rich option for various diets, including vegetarian, gluten-free, and dairy-free plans.
Environmental and Economic Value
Russet potatoes are not just nutritious—they’re also affordable and sustainable. As one of the most economically viable crops in the United States, they contribute to both food security and accessibility. Their long shelf life also reduces food waste compared to many perishable vegetables.
Studies have shown that potatoes have a lower carbon footprint compared to rice and wheat when grown using sustainable practices. Choosing locally grown russets also supports American farmers and reduces transportation emissions.
Conclusion: Rethinking Russet Potatoes in Your Diet
The russet potatoes nutrition story is one of misjudgment turned redemption. Too often dismissed as unhealthy, these versatile tubers actually deliver significant nutritional benefits—especially when prepared with care and consumed as part of a balanced diet. Rich in potassium, vitamin C, and dietary fiber, russet potatoes support heart health, aid digestion, and provide long-lasting energy.
They may not wear the flashy label of a “superfood,” but their humble, earthy roots offer more than meets the eye. Whether you’re a home cook, athlete, or health-conscious eater, giving russet potatoes a place at your table is a smart and satisfying choice.
In an era where food trends come and go, russet potatoes remain a timeless, inexpensive, and nutritious ally in promoting well-being—one delicious bite at a time.